Glutamate Excitotoxicity Assay
Contact us for further information!
Overactivation of glutamate receptors is a fundamental mechanism in neurodegenerative diseases it impairs cellular calcium homeostasis, activates nitric oxide synthesis and generation of free radicals causing programmed cell death.
Excitotoxicity induced by glutamate serves as a dependable model in understanding neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), HIV-associated neurodegenerative disorders, and others. Excitotoxicity emerges as a common pathway in various neurodegenerative conditions, making a functional phenotypic assay an intriguing approach for targeting these diseases.
At our facility, we provide services with this assay using primary frontal cortex cultures or human iPSC-derived tri-cultures comprising glutamatergic, GABAergic neurons, and astrocytes.
Cell Culture: Experiments were performed with primary frontal cortex cultures of mouse after 28 days in vitro.
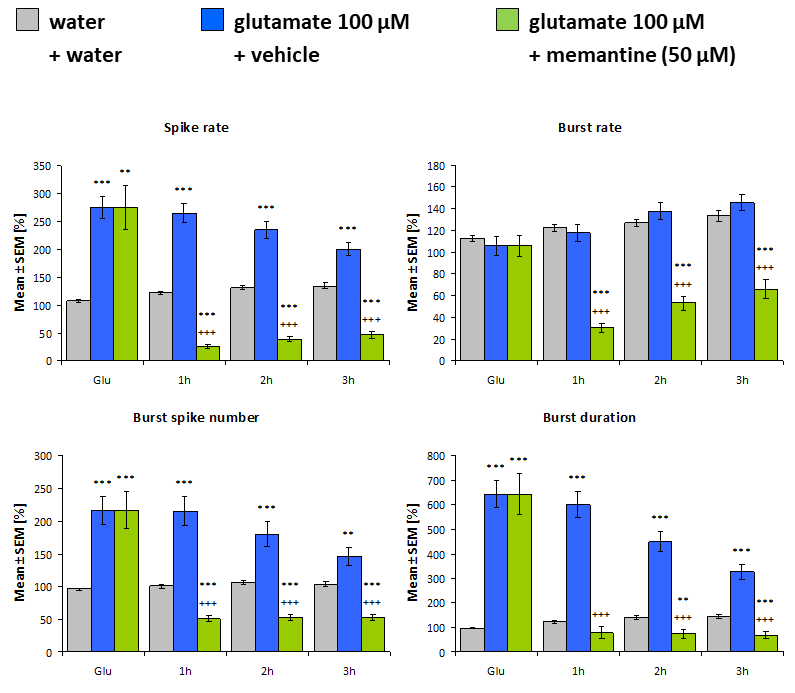
Image: Multi-parametric characterization of neuronal activity after glutamate/vehicle pretreatment and memantine/vehicle treatment (followed for 3 hours). Mean values presented with standard error. Comparison conducted using Student’s unpaired t-test against "water + water" (*) and “glutamate 100 µM + water” (+).
More Services
In addition to the primary assay, we offer supplementary or standalone assays including:
- Viability Assay: Utilizing the ToxiLight assay.
- Apoptosis: Caspase 3,Caspase 9, Bcl-2, and Bax
- Oxidative Stress Assay: Measuring 8-OHdg levels.
Explore the comprehensive suite of assays to delve deeper into neurodegenerative mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions.

 +49 381 54345-660
+49 381 54345-660
