News
New TDP 43 mislocalization assay
02 July, 2025
New TDP-43 Mislocalization Assay for ALS in Human iPSC-Derived Motor Neurons: Investigating Wildtype and C9orf72 Models

TDP-43 mislocalization and aggregation are found in 97% of ALS patients, making them key pathological features of the disease. As a result, targeting TDP-43 mislocalization represents a promising strategy for the development of new ALS therapies.
TDP-43 is an RNA and DNA-binding protein predominantly localized in the nucleus. When it is mislocalized from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, this phenomenon, known as TDP-43 mislocalization, is a hallmark of ALS.
NeuroProof has developed an advanced TDP-43 mislocalization assay utilizing automated imaging microscopy, allowing for precise quantification of TDP-43 mislocalization in motor neurons derived from human iPSCs.
In this assay, wildtype motor neurons derived from healthy donors did not exhibit TDP-43 mislocalization. However, motor neurons with the C9orf72 mutation—a key genetic cause of ALS—demonstrated significant TDP-43 mislocalization. Additionally, wildtype motor neurons exposed to arsenic also showed TDP-43 mislocalization. When C9orf72 motor neurons were treated with arsenite, mislocalization of TDP-43 remained elevated, further highlighting the mutation’s role in ALS pathology.
NeuroProof offers this innovative assay to aid in the development of novel ALS therapies, advancing our understanding of TDP-43 mislocalization as a critical target for treatment.

NeuroProof Introduces Enhanced Screening Assays with Primary Rat Neurons
12 April, 2025

NeuroProof, announces the launch of advanced screening assays featuring primary rat neurons.
One of the key questions among neurobiologists is the choice between primary rat and mouse neuronal cultures. While mice are traditionally favored in research settings, owing partly to their widespread use, the intelligence comparison between rats and mice does not alone dictate their suitability for in vitro studies. Interestingly, both rats and mice yield comparable numbers of neurons from their embryos, suggesting similar cultivation yields.
However, a notable advantage of primary rat cultures lies in their significantly higher presence of oligodendrocytes. Unlike mice, where the ratio of grey matter to white matter is approximately 90:10, rats exhibit a ratio closer to 86:14. This distinction highlights the richer presence of oligodendrocytes in rat cultures, a factor that holds substantial implications for studies related to multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and various neurological diseases.
The increased abundance of oligodendrocytes in our primary rat cultures represents a pivotal advantage for neuroscience research. It opens new avenues for exploring disease mechanisms and developing therapeutic interventions.
In response to growing demand, NeuroProof now offers primary rat cultures, with the option for enriched oligodendrocyte content upon request. This expansion underscores NeuroProof's commitment to advancing neuroscience research through innovative solutions tailored to meet evolving scientific needs.
Neuroproof and Doppelganger Launch Cutting-Edge ALS Screening Service Combining Metabolic and Electrophysiological Analysis
15 October, 2024

The Role of Energy Metabolism in ALS Progression
Energy metabolism in diseased ALS cells is severely disrupted, with mitochondrial dysfunction, altered glucose and lipid metabolism, and increased oxidative stress at the core of the disease. These metabolic dysfunctions not only result from neurodegeneration but also actively contribute to disease progression. By targeting these pathways, researchers can identify promising therapeutic strategies and novel drug targets for ALS.
Innovative Technology for ALS Research
NeuroProof has been at the forefront of ALS research, developing disease models with complex iPSC-derived cell cultures that support the validation of drug targets and compound's therapeutic potential by improving predictivity in drug screening campaigns and providing customer-specific assay development. With the integration of Doppelganger's cutting-edge QSM™ platform, NeuroProof now quantifies metabolite turnover rates across 22 principal metabolic pathways, including critical aspects of cellular bioenergetics like glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS).
The QSM™ platform, validated for use with single cells and various tissue types, enables precise analysis of energy metabolism due to hyperexcitation in ALS cells. This is the first service combining NeuroProof's multielectrode array (MEA) technology with Doppelganger's metabolic phenotyping capabilities.
Comprehensive ALS Screening Services
The new ALS screening service thoroughly evaluates metabolic dysfunctions in ALS disease models. Services include:
- Validation of ALS disease models
- Predictivity improvement in drug screening campaigns
- Single-assay prescreening for potential therapeutic compounds
This unique combination of electrophysiological and metabolic analyses delivers a comprehensive understanding of how compounds impact key metabolic pathways, such as ATP production, pyruvate, branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), and fatty acid metabolism. The data generated through these studies offer valuable insights for developing therapeutic interventions, including dietary strategies tailored to ALS patients.
Contact Us for More Information
For further details about our innovative ALS screening service and how it can support your research, please contact us. Discover how functional neuro-metabolic can unlock new potential in ALS treatment development.
About NeuroProof Systems GmbH
NeuroProof is a leader in developing biomarker assays for neurodegenerative diseases, particularly ALS. With cutting-edge electrophysiological techniques and metabolic screening technologies, NeuroProof is dedicated to improving the predictivity and efficacy of therapeutic development.
Doppelganger specializes in advanced metabolic phenotyping technologies. Its QSM™ platform, used across various disease areas, enables precise metabolic turnover rate analysis and provides critical insights into cellular energy dynamics.
NeuroProof and BrainXell at the ALS Drug Development Summit in Boston
21 May, 2024
NeuroProof Systems GmbH and BrainXell Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, collaborate to develop innovative in vitro assays on the basis of:
- BrainXell's human iPSC-derived spinal motor neurons, astrocytes, and microglia from patients with C9orf72, SOD1, TDP-43, and FUS mutations.
- NeuroProof has optimized differentiation and cultivation of these cells on microelectrode arrays and microscopic plates.
- Long-term cultivation shows a reproducible and substantial readout for electrophysiology, microscopy, and molecular biomarkers.
- NeuroProof has performed successful projects with more than 30 customers.
In Boston, we present:
- How long-term cultivation gains hyperexcitation behavior in diseased cultures. Hyperexcitation seems to be the strongest functional phenotypic readout in ALS.
- Examples of compounds that demonstrate the predictive capacity of our assays.
- Examples of our new microscopy assays for TDP-43 mislocalization and as neurite outgrowth is an additional biomarker to assess a compound's therapeutic potential.
TDP-43 Proteins in Axons of C9orf72 Mutations are Validating iPSC-Derived Motor Neurons as a Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
16 June, 2022
C9orf72 motor neurons exhibit TDP-43 condensates in somas and axons.
ALS pathology is only partially understood. TDP-43 proteins play an essential role in the mechanisms of this severe disease. Some evidence indicates that TDP-43 is an early marker of this disease starting from the neuromuscular junction.
NeuroProof investigated several markers of ALS in an automated imaging approach with the CQ1 system from Yokogawa in collaboration with Cenibra GmbH. In this study, TDP-43 was present in axons in C9orf72 spinal motor neurons, which is in concordance with other publications.
Phenotypic screening of human iPSC-derived motor neurons from patients with familial history is an excellent opportunity for screening new therapies for this severe disease.
NeuroProof has tested diseased ALS motor neurons with and without co-cultures of astrocytes in several screening assays besides its electrophysiological screening on its microelectrode array recording platform.
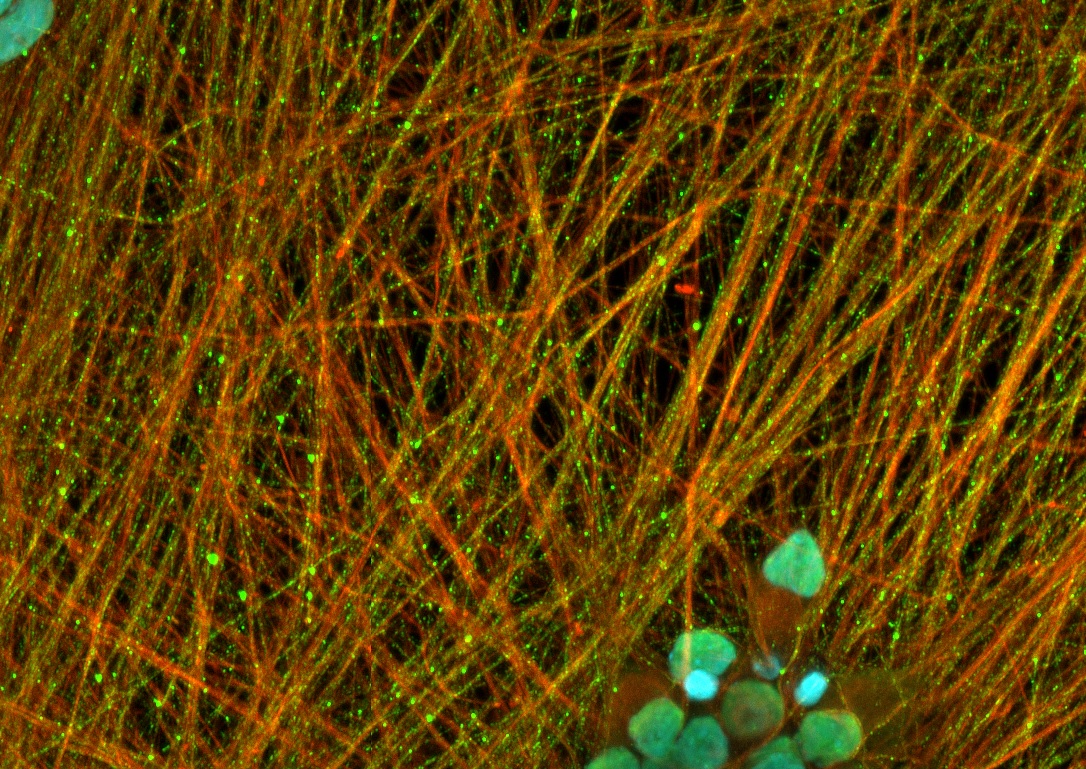
In the picture, we have stained C9orf72 human iPSC-derived motor neurons after 14 days in vitro with a TDP-43 antibody (green, nuclei with DAPI in blue, and cytoskeleton with ß-III-Tubulin in red).
Visit us at SfN meeting Nov. 12-16, 2022 in San Diego
15 June, 2022
Nov 12 at 1:00 PM
Functional Phenotypic Screening of Small Molecules in a human patient-derived cell model for Fragile X Syndrome
We developed a functional phenotypic assay with a diseased human cell line from a fragile X patient.
Cortical neurons derived from this disease cell line showed clear functional different activity patterns compared to a wild-type cell line.
We screened more than 200 compounds in this model with an MEA screen.
We identified the phosphodiesterase 10A inhibitor balipodect (TAK-063) as a potential new treatment for FXS.
We compared the potential therapeutic effects of balipodect, mavoglurant, arbaclofen, and lovastatin with this model.
Nov 16 at 8.00 AM
Functional Phenotypic Screening Models for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with human iPSC-derived spinal motor neurons
Compared to wild-type cell lines, the hyper excitation of diseased ALS cell lines with a C9orf72 and a SOD1 mutation is shown.
The effect of astrocytes on neuronal activity was investigated.
The effects of riluzole and spermidine in these models are shown.
Nov 16 at 8:00 AM
Validation of Models for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with human iPSC Motor-derived Neurons
Mislocalization of TDP-43 proteins in axons and dendrites is a hallmark of ALS. TDP-43 mislocalizations exist in iPSC-derived spinal motor neurons with C9orf72 mutations but not in wild-type motor neurons.
In the picture, we have stained C9orf72 human iPSC-derived motor neurons after 14 days in vitro with a TDP-43 antibody (green, nuclei with DAPI in blue, and cytoskeleton with ß-III-Tubulin in red).
C9orf72 mutant cells show increased levels of Poly(GR) dipeptides as a second hallmark.
Visit our presenter and discuss our new developments.

 +49 381 54345-660
+49 381 54345-660